Since its discovery in 1908, monosodium glutamate (MSG) has been used safely as a food ingredient and seasoning.
Extensive scientific research has been conducted regarding MSG safety and its role in the diet.
Based on this research, there is general consensus in the scientific community and regulators around the world that MSG is safe for everyone, including children as well as pregnant and nursing women.
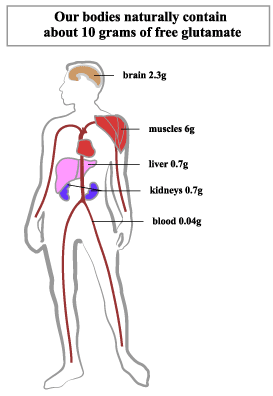 The human body metabolizes added glutamate (MSG) in the same manner it metabolizes the glutamate found naturally in many foods. Once glutamate is ingested, the body does not distinguish between the origins of the glutamate. Further, studies with infants and children in particular show they metabolize glutamate in just the same way as adults and therefore do not display any special susceptibility to elevated oral intakes of glutamate.
The human body metabolizes added glutamate (MSG) in the same manner it metabolizes the glutamate found naturally in many foods. Once glutamate is ingested, the body does not distinguish between the origins of the glutamate. Further, studies with infants and children in particular show they metabolize glutamate in just the same way as adults and therefore do not display any special susceptibility to elevated oral intakes of glutamate.
Human breast milk, the sole source of nutrition for most children in their early months, is very rich in free glutamate. It is a taste infants naturally prefer. In fact, human breast milk contains 6 to 9 times more glutamate than cow’s milk. Also, a newborn, breast-fed infant consumes free glutamate at levels far higher, for its weight, than people do from food later in life.
Scientists have investigated the effect of MSG consumption on lactation and breast-fed infants. In lactating women who consumed MSG at 100 mg/kg of body weight, researchers found no increase in the level of glutamate in human milk, and no effect on the infant’s intake of glutamate. In December 1993 the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs reviewed the effects of food and environmental agents on breastfeeding. In the report, the Committee stated that MSG has no effect on lactation and poses no risk to the consuming infant. (Pediatrics, 93:137- 150, 1994)
MSG Safety Affirmed Worldwide
MSG is one of the most thoroughly studied food ingredients in the food supply. The safety of monosodium glutamate has been reviewed and affirmed by scientists and regulatory authorities around the world.
 In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration includes MSG on its “Generally Recognized As Safe” (GRAS) list.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration includes MSG on its “Generally Recognized As Safe” (GRAS) list.
Also, the Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization (WHO) has placed MSG in its safest category for food additives. The European Community’s (EC) Scientific Committee for Foods also has confirmed the safety of monosodium glutamate.
Are consumers misinformed about MSG safety? Find out more: Kids and MSG: Relax, It’s OK, Even Good and What Are the Chances You Are Uniquely Sensitive to MSG?. Both articles are by Dr. Keith Ayoob, an internationally known nutritionist and an Associate Clinical Professor of Pediatrics at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Questions about so-called MSG allergy?, or MSG sensitivity? Read here.


